Microgrid Market: The Future of Localized Energy Independence
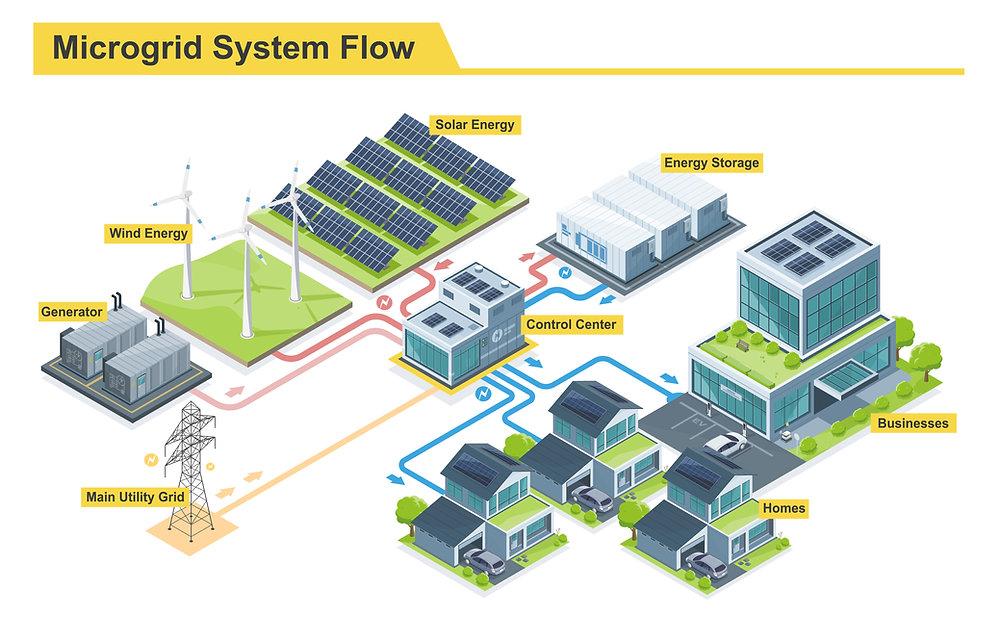
Introduction
The Microgrid Market is emerging as a cornerstone of the modern energy landscape, enabling localized, resilient, and efficient power generation and distribution. A microgrid is a self-sufficient energy system that integrates renewable sources, energy storage, and conventional power to supply electricity to a defined area such as a campus, community, or industrial zone. As global focus shifts toward energy security, sustainability, and decarbonization, the deployment of microgrids is accelerating across both developed and developing regions. The growing frequency of grid outages, rising renewable penetration, and increased emphasis on rural electrification are propelling this market forward.
Market Drivers
One of the primary drivers of the Microgrid Market is the growing demand for reliable and resilient power systems. Extreme weather events and natural disasters often disrupt traditional grids, prompting investment in decentralized systems capable of independent operation. The integration of renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and biomass within microgrids supports the global push toward reducing carbon emissions and dependence on fossil fuels.
Additionally, government policies promoting clean energy and rural electrification programs in regions like Asia-Pacific and Africa are accelerating market adoption. Advances in energy storage technologies, particularly lithium-ion batteries, enhance microgrid flexibility and energy management. The industrial and defense sectors are also key drivers, as they require uninterrupted power for mission-critical operations.
Market Challenges
Despite strong growth prospects, the market faces challenges related to high initial investment costs and complex system integration. The design, installation, and maintenance of microgrids require significant capital and technical expertise, often limiting adoption in developing economies. Regulatory uncertainty and the absence of standardized frameworks for grid interconnection and power trading also pose barriers.
Cybersecurity risks associated with digital control systems represent another major concern. As microgrids rely on advanced communication and data management technologies, ensuring protection against cyber threats becomes crucial for their sustainable operation.
Opportunities
The future offers vast opportunities for the microgrid market, particularly with the adoption of advanced control and optimization software powered by artificial intelligence and machine learning. Integration with Internet of Things (IoT) and smart meters allows real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance, improving performance and cost efficiency.
The rise of renewable hybrid microgrids, which combine multiple generation sources with energy storage, presents new possibilities for both remote and urban areas. Furthermore, corporate sustainability goals and the global shift toward carbon neutrality are encouraging industries and commercial facilities to invest in private microgrids. Emerging business models like Energy-as-a-Service (EaaS) are expected to make microgrid adoption more financially accessible.
Regional Insights
The Asia-Pacific region dominates the global microgrid market, driven by rapid urbanization, increasing energy demand, and strong government support for rural electrification. Countries such as India, China, and Indonesia are investing heavily in renewable-based microgrid systems.
North America remains a major player, particularly the United States, where universities, military bases, and commercial complexes are adopting microgrids for resilience and energy cost reduction. Europe is witnessing growth due to its ambitious decarbonization targets and emphasis on grid modernization. Meanwhile, Africa and Latin America are focusing on off-grid microgrids to address power shortages and expand energy access in remote communities.
Future Outlook
The Microgrid Market is expected to witness exponential growth in the coming decade, fueled by energy transition policies, technological innovation, and increasing investments in distributed energy resources (DERs). The integration of renewables, advanced storage solutions, and digital control technologies will enhance grid stability and efficiency.
As the global economy shifts toward decentralized and low-carbon energy systems, microgrids will play a critical role in shaping the next-generation power infrastructure. Collaborative efforts among governments, utilities, and technology providers will further unlock the market’s full potential.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Microgrid Market represents a paradigm shift in energy generation and distribution. While high costs and regulatory hurdles persist, continuous advancements in renewable integration, storage, and digital control are making microgrids more efficient and scalable. Their ability to deliver clean, reliable, and independent power makes them indispensable for a sustainable energy future. With increasing adoption across industrial, commercial, and community applications, microgrids are redefining how the world approaches power resilience and sustainability.





